Marine Corps
U.S. Military Initiates Regional Sustainment Framework with Indo-Pacific Allies
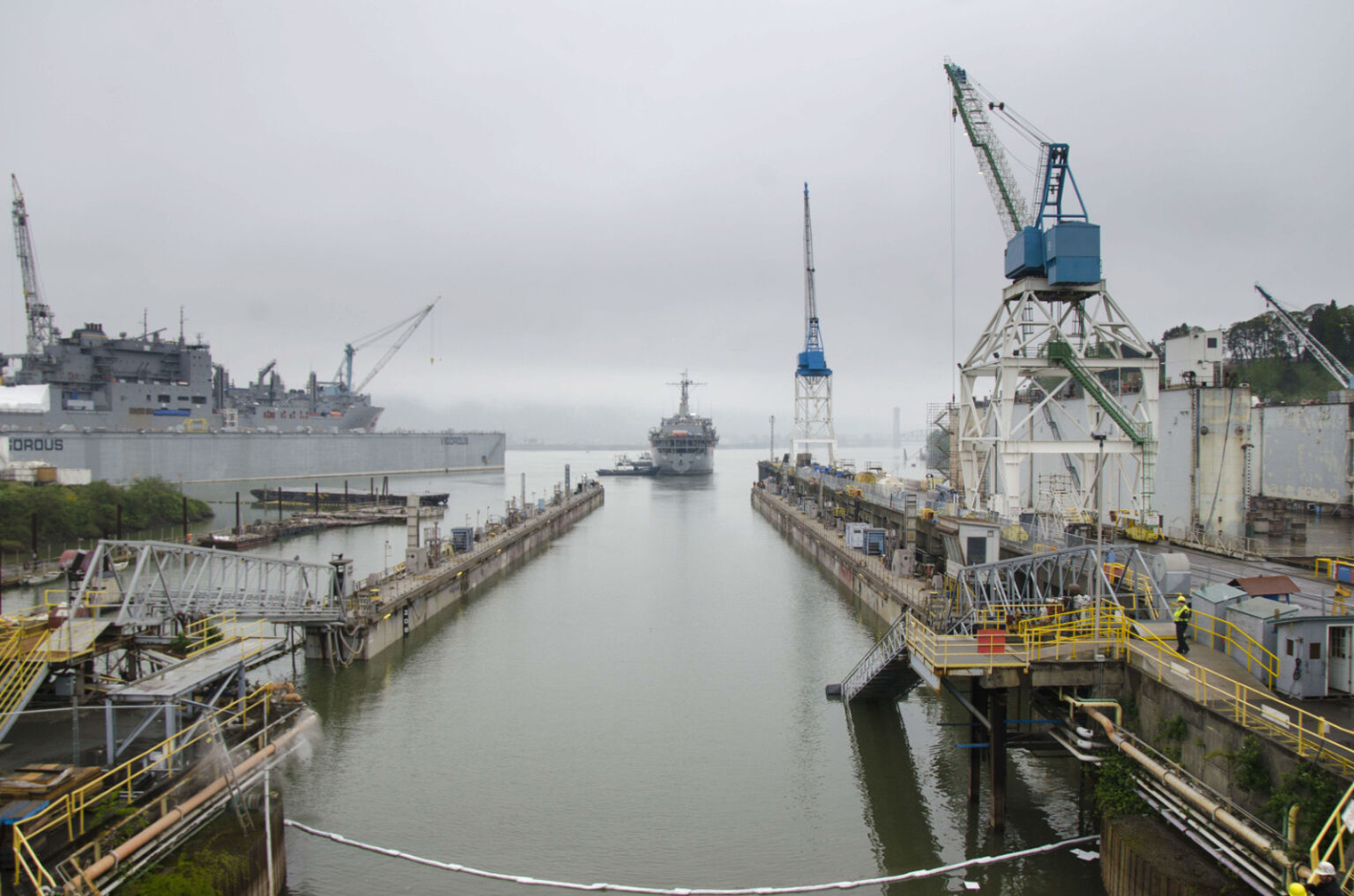

In a strategic move to enhance global military readiness, the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) announced the launch of a regional sustainment framework aimed at developing a worldwide network of regionally aligned maintenance, repair, and overhaul capabilities. The announcement was made by Christopher J. Lowman, the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Sustainment, and Lisa P. Smith, the Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense for Product Support, during a Pentagon briefing yesterday.
Key Objectives and Guiding Principles
The core principle of the regional sustainment framework is to place sustainment capabilities close to where they are needed, reducing the time and logistics involved in repairing non-mission capable equipment. “This is all about repairing damaged or non-mission capable equipment back into service,” Lowman emphasized. The initiative is designed to enhance the military capabilities of the joint force and strengthen regional partnerships through localized sustainment centers.
Collaboration with Indo-Pacific Nations
DOD is collaborating with five Indo-Pacific nations to establish these regional sustainment centers. These partners must possess the capability to repair U.S. joint force equipment and that of similarly equipped allied and partner forces. This localized approach aims to eliminate the need to transport equipment from regions like the Philippines back to the United States for repair or refurbishment, thereby increasing efficiency and readiness.
Benefits of the Framework
- Enhanced Partnerships: Strengthens U.S. relationships with regional allies.
- Increased Readiness: Improves the readiness of deployed American forces by reducing repair times.
- Deterrence: Creates higher uncertainty within adversaries’ planning cycles, enhancing deterrence capabilities.
- Collaboration with Industry: Boosts military readiness through collaboration with the U.S. industrial base.
Implementation Phases
- Indo-Pacific Command (Indo-Pacom): Focus for 2024.
- European Command (EUCOM): Focus for 2025.
- Southern Command (SOUTHCOM): Focus for 2026.
- Central Command (CENTCOM) and Africa Command (AFRICOM): Subsequent years.
Strategic Importance
Lisa P. Smith highlighted the necessity of this framework in response to evolving global threats. “The framework supports U.S. National Defense Strategy priorities and objectives by strategically engaging with our allies and partners to bring critical weapons system maintenance, repair, and overhaul capability and capacity closer to the forward-deployed point of need,” Smith stated.
Conclusion
The regional sustainment framework represents a significant shift in the U.S. military’s approach to equipment maintenance and repair, focusing on proximity and efficiency. By leveraging regional capabilities and enhancing partnerships, the U.S. aims to improve military readiness and deter potential aggression more effectively.
For further details or inquiries, please contact the Department of Defense’s media relations team.